Do not be Afraid of Arrays
A brief summery of arrays that APCSA
students should know.
Alexander Kareev
2nd hour
APCSA
05/14/06
I certify that have neither given nor received unauthorized assistance on this test or assignment .
![]()
![]()

( A
picture of me, Alex Kareev. Student of
This web page was created as part of the curriculum for the AP computer Science A (APCSA) class. I am a student finishing this class and I decided to cover the topic of Arrys as the web page topic. You can contact me at A_KAREEV@FAYAR.net and you can contact my teacher David A. Young at dyoung7@prodigy.net and or dyoung@fayar.net .
I thought that array is a very important subject from the point of view of the AP test as well ass from the point of view of a programming, so I am going to give a brief intro with links to further study. I try not to be to technical, so do not laugh ( at least not to much) on the analogies I will try to make.
Arrays can be one or two dimensional. APCSA covers only one dimensional ones. The integer type of array that deal with whole variables is the most popular one for the AP people. Technically array is a list of variables with a set size , like a column in Excel but with set size ( Arraylists are different they do not have a set size and can only deal with objects and not variables and are not covered here) .
One of the basic operations that students have to perform with arrays are to fill them and also to look for variables in them. This will prove most useful for those who understand a bit about arrays and just want to find out how to do this most frequently asked task( if you do not understand now keep reading and then come back to this paragraph).
The way to solve those two different problems of simple search and consequential fill of an array can be done with a simple for command .
for (i=0; i<array.lenth, i++){}
so if you want to fill an array it can be done like this
for (i=0; i<array.lenth, i++){
array[i}= 2i;
}
What this does is that it goes thought the arrays and assigns a double value of I which is increasing by one on each round.
This would create a list of arrays 0,2,4,…… (depending on the length of this array)
Search can be done similarly
while ( a != 5){
for (i=0; i<array.lenth, i++){
array[i]= a;
}
}
return i;
This line of code assigns a value of different values in one dimensional array to the value of a till the a is not equal to the searched value, which is 5 here . then the i value is returned to tell where this was found.
This is a simple code and could create an infinite loop if there is no value 5 in array. There are a lot of ways to avoid this and get the result
One way to avoid infinite loop is to change while statement
to one like this for example
while ( a != 5 || a==array.lenth ){ }
And that is how to solve the most asked for problems.
And now lets go to more detailed and step by step overview of
arrays.
This I think is the best and shortest overview of arrays from the Sun tutorial webpage and it could be found here.
( at first I wanted to summarize it, but then realized that it is perfect as it is)
http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/java/data/arrays.html
Picture of the idea of array from this site
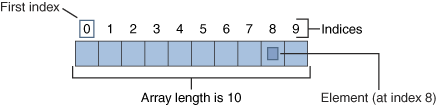
To find out more about the methods of the array and the class itself go here. It has mountains of raw information, but you need to be familiar with API to read it. Some of the most common methods used by AP testers is length .
Array.lenght(gives value of length of array)
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.3/docs/api/java/lang/reflect/Array.html
Previous link was to language package that game methods to array. Here is the length to the java.utill.Arrays which is more specific
http://java.sun.com/j2se/1.4.2/docs/api/java/util/Arrays.html
here is the link of more down to earth description of array class but it goes more by illustrations, the code is simple once you look, so do not get scared away, there aresome good examples here.
http://www.ruby-doc.org/core/classes/Array.html
Arrays are very useful to store data for the program to use as well as get data from the user. For example some games like tic tack toe one created as a program may use an array this way the array can be 8 in length (0-7) and be filled with zero for empty one for cross and 2 for not and then simple comparison would tell who won. Arrays are also used with pointers to detect the location of mouse on screen (in Applets mostly). Here is a link to this idea, it is complicated but puts arrays in perspective.
http://home.netcom.com/~tjensen/ptr/pointers.htm
Wikipedia took a stub at defining arrays for programming here is the link. This looks interesting but I am not sure how useful it will be for you.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Array
And here is the link to a slightly different use of arrays, the ones for Java script the principle is the same but may be more useful and practical for some
www.pageresource.com/jscript/jarray.htm
And of course here is the length to the D. A. Y’s home page for APCSA 2005-2006. At the bottom there is a chapter 13 power pint that does a beautiful job of explaining the arrays.
http://fayar.net/east/teacher.web/Math/young/APCSA0506.html
Thank you for visiting the webpage. I hope it proved useful.
This beautigull picture of the Java coffe cup was taken from another student’s webpage

Here is the link
http://fayar.net/east/teacher.web/Math/young/JAVA/DK/Javasort.html